Physical electronics devices and ics miscellaneous
- If the load resistance decreases in a zener regulator, the zener current—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
If the load resistance decreases in a zener regulator the zener current increases because

Correct Option: B
If the load resistance decreases in a zener regulator the zener current increases because
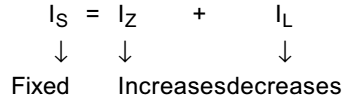
- Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists—
List-I
(a) Gunn Diode
(b) Solar Cell
(c) MOSFET
(d) SCR
List-II
1. Junctionless device
2. Single junction device
3. Double junction device
4. Triple junction device Codes:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
● Gunn diode → Junction less device
● Solar cell → Single junction device
● MOSFET → Double junction device
● SCR → Triple junction deviceCorrect Option: A
● Gunn diode → Junction less device
● Solar cell → Single junction device
● MOSFET → Double junction device
● SCR → Triple junction device
- Match List-I (Diode type) with List-II (Important properties) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists—
List-I
(a) Zener Diode
(b) Gunn Diode
(c) Schottky Diode
(d) Tunnel Diode
List-II
1. Negative resistance device fabricated using semiconductors like Si, Ga, As, Ge etc. can be operated at a frequency of 10 GHz.
2. Quantum mechanical tunnelling with very thin depletions layers under reverse bias operated as a reference voltage sources.
3. Negative conductance device, operates on the principle of transfer of electron from one region of conduction band to another.
4. Metal-semiconductor diode, have rectification properties. Codes:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
● Zener diode → Quantum mechanical tunnelling with very thin depletion layers under reverse bias operated as a reference voltage sources.
● Gunn diode → Negative conductance device, operates on the principle of transfer of electrons from one region of conduction band to another.
● Schottky Diode → Metal-semiconductor diode, have rectification properties.
● Tunnel diode → Negative resistance device fabricated using semiconductors like Si, Ga, As, Ge etc. can be operated at a frequency of 10 GHz.Correct Option: C
● Zener diode → Quantum mechanical tunnelling with very thin depletion layers under reverse bias operated as a reference voltage sources.
● Gunn diode → Negative conductance device, operates on the principle of transfer of electrons from one region of conduction band to another.
● Schottky Diode → Metal-semiconductor diode, have rectification properties.
● Tunnel diode → Negative resistance device fabricated using semiconductors like Si, Ga, As, Ge etc. can be operated at a frequency of 10 GHz.
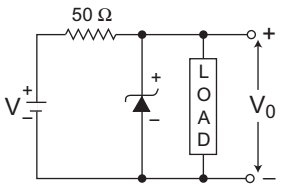
- A zener diode in the circuit shown in the figure below, has a knee current of 5 mA and a maximum allowed power dissipation of 300 mW. What are the minimum and maximum load currents that can be drawn safely from the circuit, keeping the output voltage V0 at 6 V?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The given circuit (i.e., fig)
Given, IZK = 5 mA, V0 = VZ = 6V, RS = 50 Ω, Vi = 9VPZM = 300 mW or IZ(max) = PZM = 300 mW = 64 mA VZ 6V
= 50 mAFrom figure, I S = Vi – VZ = 9 - 6 = 3 = 60 mA RS 50 50
Now, IL(min) = IS – IZ(max) = 60 – 50 = 10 mA
IL(max) = IS – IZK = 60 – 5 = 55 mA
Hence alternative (C) is the correct choice.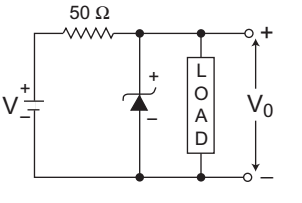
Correct Option: C
The given circuit (i.e., fig)
Given, IZK = 5 mA, V0 = VZ = 6V, RS = 50 Ω, Vi = 9VPZM = 300 mW or IZ(max) = PZM = 300 mW = 64 mA VZ 6V
= 50 mAFrom figure, I S = Vi – VZ = 9 - 6 = 3 = 60 mA RS 50 50
Now, IL(min) = IS – IZ(max) = 60 – 50 = 10 mA
IL(max) = IS – IZK = 60 – 5 = 55 mA
Hence alternative (C) is the correct choice.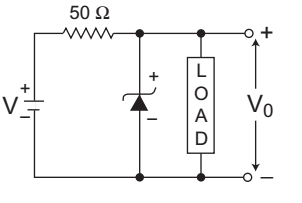
- Match List-I (Devices) with List-II (Property) and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists—
List-I
(a) Silicon diode
(b) Germanium diode
(c) LED
(d) PIN diode
List-II
1. High frequency applications
2. Very low reverse bias saturation current
3. Low forward bias voltage drop
4. Cut-off wavelength Codes:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
● Silicon diode → Very low reverse bias
● Germanium diode → Low forward bias voltage drop
● LED → Cut-off wavelength
● PIN diode → High frequency applicationsCorrect Option: D
● Silicon diode → Very low reverse bias
● Germanium diode → Low forward bias voltage drop
● LED → Cut-off wavelength
● PIN diode → High frequency applications

