Materials Science and Manufacturing Engineering Miscellaneous
Direction: Orthogonal turning is performed on a cylindrical workpiece with shear strength of 250 MPa. The following conditions are used: cutting velocity is 180 m/min, feed is 0.20 mm/rev, depth of cut is 3 mm, chip thickness ratio = 0.5. The orthogonal rake angle is 7°. Apply Merchants theory for analysis.
- The shear plane angle (in degrees) and the shear force respectively are
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
tanφ= rcosα = 0.5 × cos7° = 0.503 1 − rsinα 1 − 0.5sin7°
φ = 28°
Now, shear force = shear stress × area
F = 250 × AB width of cut
∴ AB = AC = 0.2 = 0.43 sin28° sin28°
where AC is incut chip thickness
Now width ≌ depth of cut = 3 mm
F = 250 × 0.43 ×3
≌ 320 NCorrect Option: D
tanφ= rcosα = 0.5 × cos7° = 0.503 1 − rsinα 1 − 0.5sin7°
φ = 28°
Now, shear force = shear stress × area
F = 250 × AB width of cut
∴ AB = AC = 0.2 = 0.43 sin28° sin28°
where AC is incut chip thickness
Now width ≌ depth of cut = 3 mm
F = 250 × 0.43 ×3
≌ 320 N
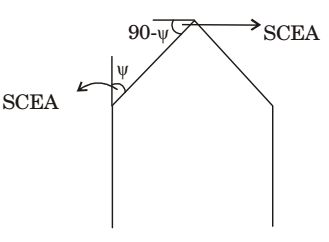
- In a single point turning tool, the side rake angle and orthogonal rake angle are equal. φ is the principal cutting edge angle and its range is 0° ≤ φ ≤ 90°. The chip flows in the orthogonal plane. The value of φ is closest to
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Side rake angle is equal to orthogonal rake angle when principle cutting edge angle become 90° and corresponding approach angle SCEA = 0°
Correct Option: D
Side rake angle is equal to orthogonal rake angle when principle cutting edge angle become 90° and corresponding approach angle SCEA = 0°

Direction: A low carbon steel bar of 147 mm diameter with a length of 630 mm is being turned with uncoated carbide insert. The observed tool lives are 24 min and 12 min for cutting velocities of 90 m/min and 120 m/min respectively. The feed and depth of cut are 0.2 mm/ rev and 2 mm respectively. Use the unmachined diameter to calculate the cutting velocity.
- Neglect over-travel or approach of the tool. When tool life is 20 min, the machining time in min for a single pass is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
V = πDN
N =210.2 rpm
∴ Machining time,tm= L = .15min. N Correct Option: C
V = πDN
N =210.2 rpm
∴ Machining time,tm= L = .15min. N
- When tool life is 20 min, the cutting velocity in m/min is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Here, D = 147 mm, L = 630 mm,
f = .2 mm/rev,
d = 2 mm
Tool life equation,
VTn = constant
Now, V1T1n = V2T2n
Here, n = .415
∴ VTn = V1T1n
⇒ V =97.07 m/minCorrect Option: B
Here, D = 147 mm, L = 630 mm,
f = .2 mm/rev,
d = 2 mm
Tool life equation,
VTn = constant
Now, V1T1n = V2T2n
Here, n = .415
∴ VTn = V1T1n
⇒ V =97.07 m/min
- In orthogonal turning of low carbon steel pipe with principal cutting edge angle of 90°, the main cutting force is 1000 N and the feed force is 800 N. The shear angle is 25° and orthogonal rake angle is zero. Employing Merchants theory, the ratio of friction force to normal force acting on the cutting tool is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Here, φ = shear angle = 25º
λ = Friction angle,
α =rake angle = 0º
From Merchant’s theory, 2φ + λ − α = 90º
∴ λ = 90º – 50º = 40º∴ μ = F = Friction force = tan λ = .83 N Normal force Correct Option: C
Here, φ = shear angle = 25º
λ = Friction angle,
α =rake angle = 0º
From Merchant’s theory, 2φ + λ − α = 90º
∴ λ = 90º – 50º = 40º∴ μ = F = Friction force = tan λ = .83 N Normal force

