Analog electronics circuits miscellaneous
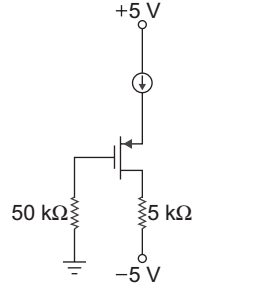
- The parameter of the transistor in fig. below are VTN = 0.6 V and Kn = 0.2 mA/V2. The voltage Vs is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given that VTN = 0.6 V
Kn = 0.2 mA/V2
ID = 0.25 mA
ID = Kn (VGS – VTn)2
0.25 × 10– 3 = 0.2 × 10– 3 (VGS – 0.6)225 = (VGS – 0.6)2 20 VGS = 5 + 0.6 = 1.718 ≈ 1.72 √20
VG = 0 V
VGS = VG – VS
or VS = VG – VGS = 0 – 1.72 = – 1.72 V
Hence (B) is the correct choice.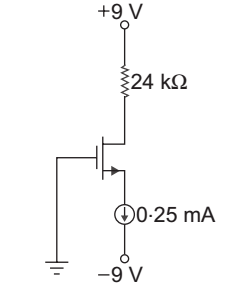
Correct Option: B
Given that VTN = 0.6 V
Kn = 0.2 mA/V2
ID = 0.25 mA
ID = Kn (VGS – VTn)2
0.25 × 10– 3 = 0.2 × 10– 3 (VGS – 0.6)225 = (VGS – 0.6)2 20 VGS = 5 + 0.6 = 1.718 ≈ 1.72 √20
VG = 0 V
VGS = VG – VS
or VS = VG – VGS = 0 – 1.72 = – 1.72 V
Hence (B) is the correct choice.
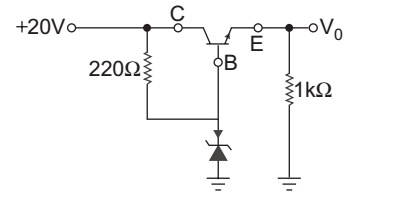
- In the regulator circuit of fig. below Vz = 12 V, β = 50, VBE = 0.7 V. The Zener current is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
V0 = VZ – VBE
= 12 – 0.7 = 11.3 V
VCE = 20 – 11.3 = 8.7 V
Current in 220 Ω resistor isI220 Ω = 20 – 12 = 36.4 mA 220
Current in 1 kΩ resistor is11kΩ = V0 = 11·3 = 11.3 mA = IC 1 kΩ 1 kΩ IB = IC = 11·3 = 0.226 mA β 50
KCL at node A, we get
IZ = I220 Ω – IB = 36.4 – 0.226 = 36.17 mA
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.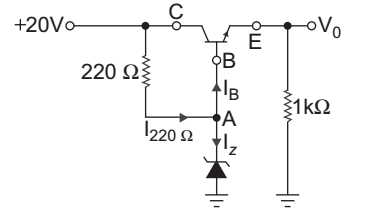
Correct Option: B
V0 = VZ – VBE
= 12 – 0.7 = 11.3 V
VCE = 20 – 11.3 = 8.7 V
Current in 220 Ω resistor isI220 Ω = 20 – 12 = 36.4 mA 220
Current in 1 kΩ resistor is11kΩ = V0 = 11·3 = 11.3 mA = IC 1 kΩ 1 kΩ IB = IC = 11·3 = 0.226 mA β 50
KCL at node A, we get
IZ = I220 Ω – IB = 36.4 – 0.226 = 36.17 mA
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.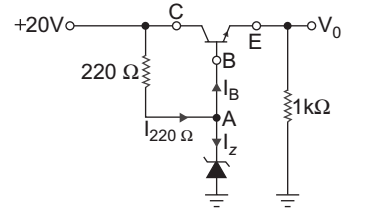
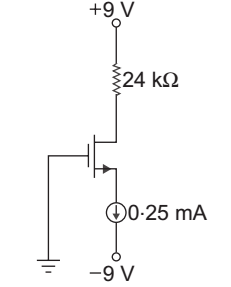
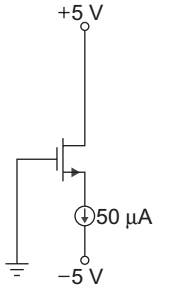
- The parameter of the transistor in fig given below VTN = 1.2 V, Kn = 0.5 mA/V2. The voltage VDS is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given that VTN = 1.2 V
Kn = 0.5 mA/V2
ID = Kn (VS – VTN)2
50 × 10– 6 = 0.5 × 10– 3 (VGS – 1.2)2
VGS = √.1 + 1.2 = 1.516 V
VG = 0
so VGS = VG – VS
or VS = VG – VGS = 0 – 1.516
= – 1.516 V
VDS = VD – VS = 5 – (– 1.516)
= 6.516 V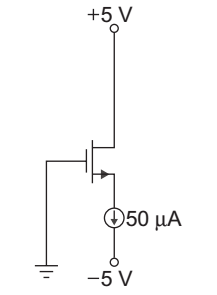
Correct Option: B
Given that VTN = 1.2 V
Kn = 0.5 mA/V2
ID = Kn (VS – VTN)2
50 × 10– 6 = 0.5 × 10– 3 (VGS – 1.2)2
VGS = √.1 + 1.2 = 1.516 V
VG = 0
so VGS = VG – VS
or VS = VG – VGS = 0 – 1.516
= – 1.516 V
VDS = VD – VS = 5 – (– 1.516)
= 6.516 V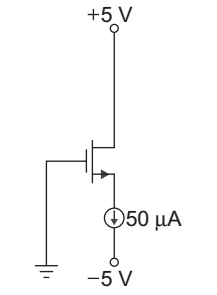
Direction: Statement for :
In the circuit of fig. below the transistor parameters are VTP = – 0.8 V and KP = 200 µA/V2

- VSD =?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
VD = ID RD – 5 = 0.4 × 10– 3 × 5 × 103 – 5 = – 3 V
VSD = VS – VD = 2.21 – (– 3) = 5.21 V
Hence alternative (A) is the correct choice.Correct Option: A
VD = ID RD – 5 = 0.4 × 10– 3 × 5 × 103 – 5 = – 3 V
VSD = VS – VD = 2.21 – (– 3) = 5.21 V
Hence alternative (A) is the correct choice.
- VS =?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Assume transistor in saturation
given, ID = 0.4 mA
VTP = – 0.8 V
kP = 200 µA/V2
ID = kP [VSG + (– VTP)]2
0.4 × 10–3 = 200 × 10–6 [VSG + 0.8]2
or [VSG + 0.8]2 = 2
or VSG = √2 + 0.8 = 2.21 V
or VSG = VS – VG = VS – 0 = VS
= 2.21 V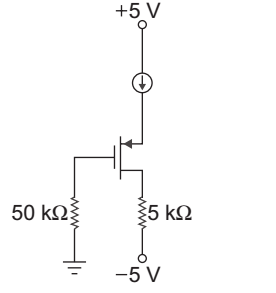
Correct Option: C
Assume transistor in saturation
given, ID = 0.4 mA
VTP = – 0.8 V
kP = 200 µA/V2
ID = kP [VSG + (– VTP)]2
0.4 × 10–3 = 200 × 10–6 [VSG + 0.8]2
or [VSG + 0.8]2 = 2
or VSG = √2 + 0.8 = 2.21 V
or VSG = VS – VG = VS – 0 = VS
= 2.21 V