Analog electronics circuits miscellaneous
- For the circuit shown below each diode has Vr = 0.6 V and rf = 0. Both diode will be ON if:

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
VA = VS. 500 = VS 500 + 5000 11
and given cut-in voltage i.e., Vγ = 0.6 for each diode, for VS > 0.6 V, D1 is ON., while for VA > 0.6 V, both the diode will be ON.
KCL at node A.VA – VS + 0.6 + VA – VS + VA + VA – 0.6 = 0 5 kΩ 5 kΩ 500 kΩ 500 kΩ VA = 2VS + 5.4 > 0.6 V 22
⇒ VS > 3.9 V
Hence alternative (A) is the correct choice.
Correct Option: A
VA = VS. 500 = VS 500 + 5000 11
and given cut-in voltage i.e., Vγ = 0.6 for each diode, for VS > 0.6 V, D1 is ON., while for VA > 0.6 V, both the diode will be ON.
KCL at node A.VA – VS + 0.6 + VA – VS + VA + VA – 0.6 = 0 5 kΩ 5 kΩ 500 kΩ 500 kΩ VA = 2VS + 5.4 > 0.6 V 22
⇒ VS > 3.9 V
Hence alternative (A) is the correct choice.
Direction: Consider the circuit. Assume diodes are ideal.

- If ν1 = – 5 V and ν2 = 10 V, then output voltage ν 0 is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: C
NA
- If V1 = V2 = 10 V, then output voltage ν 0 is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since both the terminal voltage at 10 V i.e., V1 = V2 = 10 V, so we assume that both D1 and D2 are ON.
Apply KCL at node A.V0 – 5 + V0 – V1 + V0 – V2 = 0 9 1 1 V0 = V1 + V2 + 5 = 9.737 V 1 1 9 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1
Check condition:= V1 – V0 = V2 – V0 = 10 – 9.737 1 1 1
= .627 A > 0
Therefore both the diodes are ON.
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.
Correct Option: B
Since both the terminal voltage at 10 V i.e., V1 = V2 = 10 V, so we assume that both D1 and D2 are ON.
Apply KCL at node A.V0 – 5 + V0 – V1 + V0 – V2 = 0 9 1 1 V0 = V1 + V2 + 5 = 9.737 V 1 1 9 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1
Check condition:= V1 – V0 = V2 – V0 = 10 – 9.737 1 1 1
= .627 A > 0
Therefore both the diodes are ON.
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.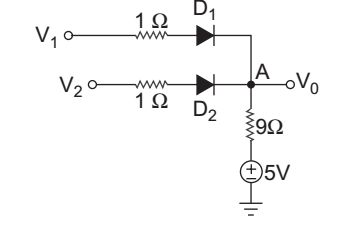
Direction: Consider the circuit Assume diodes are ideal.

- If V1 = – 5 V and V2 = 5 V then V 0 is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since given V1 = – 5 V and V2 = 5 V, so we assume that D1 is OFF and D2 is ON
V0 = V2·9 = 5 × 9 = 4.5 V 9 + 1 10
Check assumptionID1 = V2 – V0 = 5 – 4.5 1 kΩ 1 kΩ
= 0.5 mA > 0, therefore D2 is ON
VD1 = V1 – V0 = – 5 – 4.5
= – 9.5 < 0, therefore D1 is OFF Hence alternative (C) is the correct choice.
Correct Option: C
Since given V1 = – 5 V and V2 = 5 V, so we assume that D1 is OFF and D2 is ON
V0 = V2·9 = 5 × 9 = 4.5 V 9 + 1 10
Check assumptionID1 = V2 – V0 = 5 – 4.5 1 kΩ 1 kΩ
= 0.5 mA > 0, therefore D2 is ON
VD1 = V1 – V0 = – 5 – 4.5
= – 9.5 < 0, therefore D1 is OFF Hence alternative (C) is the correct choice.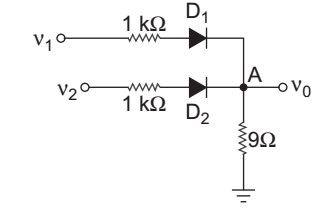
- If V1 = V2 = 10 V, then output voltage V 0 is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Since both the terminal voltage V1 and V2 is at 10 V and connected through the same 1 kΩ resistance. So in this case we assume that both the diodes are ON.
Apply. KCL at node AV0 – 0 + V0 – V1 + V0 – V2 = 0 9 1 1 or V0 = V1 + V2 1 1 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1 = 10 + 10 = 9.474 V 1 1 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1
Check assumptionID1 = ID2 = V1 – V0 = V2 - V0 = 10 – 9·474 1 kΩ 1 kΩ 1 kΩ
ID1 = ID2 = 0.526 mA > 0
Therefore Diode D1 and D2 both are ON.
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.
Correct Option: B
Since both the terminal voltage V1 and V2 is at 10 V and connected through the same 1 kΩ resistance. So in this case we assume that both the diodes are ON.
Apply. KCL at node AV0 – 0 + V0 – V1 + V0 – V2 = 0 9 1 1 or V0 = V1 + V2 1 1 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1 = 10 + 10 = 9.474 V 1 1 1 + 1 + 1 9 1 1
Check assumptionID1 = ID2 = V1 – V0 = V2 - V0 = 10 – 9·474 1 kΩ 1 kΩ 1 kΩ
ID1 = ID2 = 0.526 mA > 0
Therefore Diode D1 and D2 both are ON.
Hence alternative (B) is the correct choice.

