Analog electronics circuits miscellaneous
Direction: Consider the circuit shown below:
The both transistor have parameter as follows:
VTN = 0.8 V, kn = 30 ΩA/V2

- If the width-to-length ratios of M1 and M2 are:

W 
= 
W 
= 40 L 1 L 2
The output V0 is:
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For both transistor M1 and M2
VDS = VGS
∴ VDS > VGS – VTN therefore both the transistor are in saturation
ID1 = ID2
ID1 = Kn1 (VGS1 – VTN1 )2
= Kn2 (VGS2 – VTN2)2 …(A)
Kn1 = Kn2 and VTN1 = VTN2
on expanding equation
V2GS1 + V2TN1 – 2VGS1 = V2GS2 + V2TN2 – 2VGS2
or V2GS1 + V2GS2 = 2 (VGS1 – VGS2) …(B)
from given figure,
VGS1 + VGS2 = 5 …(C)
V2GS1 – (5 – VGS1 )2 = 2 (VGS1 – VGS1 + 5)
V2GS1 – 25 – V2GS1 + 10 VGS1 = 10
10 VGS1 = 35
or VGS1 = 3.5
VGS2 = 5 – VGS1 = 5 – 3.5 = 1.5 V
So, V0 = 5 – VGS1 = VGS2 = 1.5 V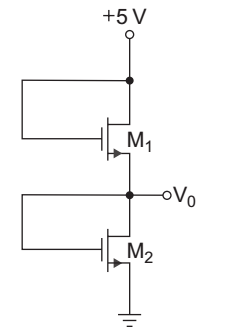
Correct Option: A
For both transistor M1 and M2
VDS = VGS
∴ VDS > VGS – VTN therefore both the transistor are in saturation
ID1 = ID2
ID1 = Kn1 (VGS1 – VTN1 )2
= Kn2 (VGS2 – VTN2)2 …(A)
Kn1 = Kn2 and VTN1 = VTN2
on expanding equation
V2GS1 + V2TN1 – 2VGS1 = V2GS2 + V2TN2 – 2VGS2
or V2GS1 + V2GS2 = 2 (VGS1 – VGS2) …(B)
from given figure,
VGS1 + VGS2 = 5 …(C)
V2GS1 – (5 – VGS1 )2 = 2 (VGS1 – VGS1 + 5)
V2GS1 – 25 – V2GS1 + 10 VGS1 = 10
10 VGS1 = 35
or VGS1 = 3.5
VGS2 = 5 – VGS1 = 5 – 3.5 = 1.5 V
So, V0 = 5 – VGS1 = VGS2 = 1.5 V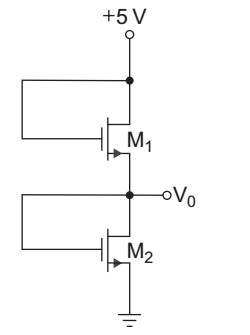
- The parameters for the transistor in circuit of fig. below are VTN = 2 V and Kn = 0.2 mA/V2. The power dissipated in the transistor is:
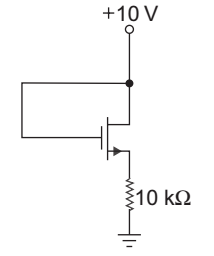
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From fig. since gate is connected to the drain. Hence transistor will always in saturation.
ID = 10 – VGS = Kn (VGS – VTn)2 10 kΩ
10 – VGS = 0.2 × 10–3 × 10 × 103 (VGS – 2)2
or 10 – VGS = 2 (VGS – 2)2
After solving quadratic equation, we get
VGS = – 0.27 V, 3.77 V VGS = – 0.27 is not possible since gate terminal is at 10 V. So, VGS = 3.77 V is taken
i.e. VGS = VDS = 3.77 VID = 10 – 3·77 = 0.623 mA 10 kΩ
Power = ID VDS = 0.623 × 10–3 × 3.77 = 2.35 mW
Correct Option: B
From fig. since gate is connected to the drain. Hence transistor will always in saturation.
ID = 10 – VGS = Kn (VGS – VTn)2 10 kΩ
10 – VGS = 0.2 × 10–3 × 10 × 103 (VGS – 2)2
or 10 – VGS = 2 (VGS – 2)2
After solving quadratic equation, we get
VGS = – 0.27 V, 3.77 V VGS = – 0.27 is not possible since gate terminal is at 10 V. So, VGS = 3.77 V is taken
i.e. VGS = VDS = 3.77 VID = 10 – 3·77 = 0.623 mA 10 kΩ
Power = ID VDS = 0.623 × 10–3 × 3.77 = 2.35 mW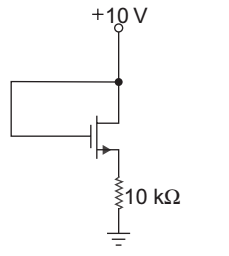
- The PMOS transistor shown below has parameters:
VTP = - 1.2 V, W = 20, and KP = 30 µA/V2 L
If ID = 0.5 mA and VD = – 3 V, then value of RS and RD are: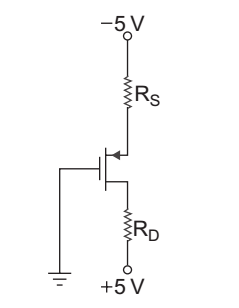
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: D
NA
- In the circuit given below the transistor parameters are:
VTN = 1.7 V and Kn = 0.4 mA/V2.
If ID = 0.8 mA and VD = 1 V, then value of resistor RS and RD are respectively: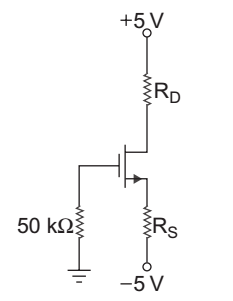
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
From figure
ID = 5 – VD RD 0.8 × 10–3 = 5 – 1 RD or RD = 4 = 5 kΩ 0·8 × 10–3
ID = Kn (VGS – VTn)2
or 0.8 × 10–3 = 0.4 × 10–3 (VGS – 1.7)2
or VGS = √2 + 1.7 = 3.11 V VG – VS = 3.11
or VS = VG – 3.11 = 0 – 3.11 = – 3.11 VAgain, ID = VS – (–5) = –3·11 + 5 RS RS or RS = 1·89 = 2.3625 kΩ 0·8 × 10–3 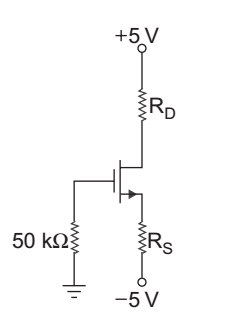
Correct Option: A
From figure
ID = 5 – VD RD 0.8 × 10–3 = 5 – 1 RD or RD = 4 = 5 kΩ 0·8 × 10–3
ID = Kn (VGS – VTn)2
or 0.8 × 10–3 = 0.4 × 10–3 (VGS – 1.7)2
or VGS = √2 + 1.7 = 3.11 V VG – VS = 3.11
or VS = VG – 3.11 = 0 – 3.11 = – 3.11 VAgain, ID = VS – (–5) = –3·11 + 5 RS RS or RS = 1·89 = 2.3625 kΩ 0·8 × 10–3 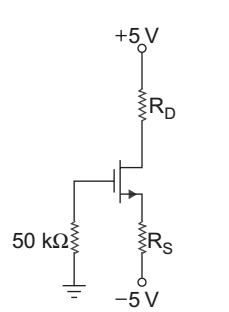
- In the circuit given below, the transistor T3 is used as:
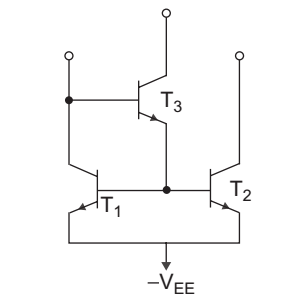
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: B
NA

