Thermodynamics Miscellaneous
- Any thermodynamic cycle operating between two temperature limits is reversible if the product of the efficiency when operating as a heat engine and the COP when operating as a refrigerator is equal to l.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
False
ηHE × COPHP = 1
Where , HP = Heat pumpCorrect Option: C
False
ηHE × COPHP = 1
Where , HP = Heat pump
- When a system executes an irreversible cycle
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
∮ δQ < 0 clausius inequality T
Correct Option: A
∮ δQ < 0 clausius inequality T
- Figure below shows a reversible heat engine ER having heat interactions with three constant temperature systems. Calculate the thermal efficiency of the heat engine
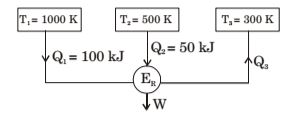
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Q1 + Q2 - Q3 = W .... (i)
Q1 + Q2 - Q3 = 0 ...... (ii) 1000 500 300
From equation (ii) , we haveQ1 + Q2 - Q3 = 0 1000 500 300
⇒ Q3 = 60 kJ
W ⇒ 100 + 50 - 60 = 90 kJ
η = W = 90 = 60% Q1 + Q2 150
Correct Option: A
Q1 + Q2 - Q3 = W .... (i)
Q1 + Q2 - Q3 = 0 ...... (ii) 1000 500 300
From equation (ii) , we haveQ1 + Q2 - Q3 = 0 1000 500 300
⇒ Q3 = 60 kJ
W ⇒ 100 + 50 - 60 = 90 kJ
η = W = 90 = 60% Q1 + Q2 150
- A reversible heat transfer demands :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
∆S = 0
⇒ δQ - δQ = 0 T1 T2
⇒ T1 = T2Correct Option: A
∆S = 0
⇒ δQ - δQ = 0 T1 T2
⇒ T1 = T2
- A condenser of a refrigeration system rejects heat at a rate of 120 kW, while is compressor consumes a power of 30 kW. The coefficient of performance of the system would be
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Q1 = 120 kW , W = 30 × kW , Q2 = 120 – 30 = 90kW

(COP)ref = Q2 = 90 = 3 W 30
Correct Option: D
Q1 = 120 kW , W = 30 × kW , Q2 = 120 – 30 = 90kW

(COP)ref = Q2 = 90 = 3 W 30

