Engineering Mathematics Miscellaneous
- The partial differential equation
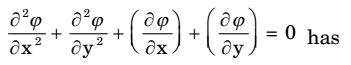
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A order is 2 and degree is 1.
Correct Option: A
A order is 2 and degree is 1.
- A differential equation is given as
x2 d2y - 2x dy + 2y = 4 dx2 dx
The solution of the differential equation in terms of arbitrary constants C1 and C2 is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
x2 = d2y - 2x dy + 2y = 4 dx2 d
Let x = ezCF : d2y = θ(θ - 1) dx2
⇒ θ(θ - 1) - 2θ + 2 = 0
⇒ θ2 - 3θ + 2 = 0
(θ - 1)(θ - 2) = 0
θ = 1,2
θ = C1ez + C1e2z
y = C1x2 + C2xPI : - 4 + 4 (θ - 1) (θ - 2) = + 4(1 -θ)-1 - 4 
1 - θ 
-1 2 2 = + 4(1 - θ + ...) - 2 
1 + θ + ..... 
2
= + 4 – 2 = 2 (Neglecting higher order term)
y = CF + PI
y = C1 x2 C2 x + 2Correct Option: C
x2 = d2y - 2x dy + 2y = 4 dx2 d
Let x = ezCF : d2y = θ(θ - 1) dx2
⇒ θ(θ - 1) - 2θ + 2 = 0
⇒ θ2 - 3θ + 2 = 0
(θ - 1)(θ - 2) = 0
θ = 1,2
θ = C1ez + C1e2z
y = C1x2 + C2xPI : - 4 + 4 (θ - 1) (θ - 2) = + 4(1 -θ)-1 - 4 
1 - θ 
-1 2 2 = + 4(1 - θ + ...) - 2 
1 + θ + ..... 
2
= + 4 – 2 = 2 (Neglecting higher order term)
y = CF + PI
y = C1 x2 C2 x + 2
- Given the ordinary differential equation
d2y + dy = 0 dx2 dx with(0) = 0 and dy (0) = 1, the value of y(1) is dx
_______ (correct to two decimal places).
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
(D2 + D – 6) y = 0
y (0) = 0,
y' (0) = 1
(D + 3) (D – 2) y = 0
D = 2, – 3
C .F. = C1 e2x + C2 e–3x
y = c1 e2x + C2 e–3x
y (0) = 0
So, 0 = C1 + C2 ----------------------(i)y = (1) = e2 - e- 3 = 1.4678 5
y (0) = 1
1 = 2 C1 – 3 C2 ___(ii)
From equations (i) & (ii), we getC1 = 1 , C2 = - 1 5 5 y = e2x - e- 3x 5 5
when, x = 1y = (1) = e2 - e- 3 = 1.4678 5 Correct Option: A
(D2 + D – 6) y = 0
y (0) = 0,
y' (0) = 1
(D + 3) (D – 2) y = 0
D = 2, – 3
C .F. = C1 e2x + C2 e–3x
y = c1 e2x + C2 e–3x
y (0) = 0
So, 0 = C1 + C2 ----------------------(i)y = (1) = e2 - e- 3 = 1.4678 5
y (0) = 1
1 = 2 C1 – 3 C2 ___(ii)
From equations (i) & (ii), we getC1 = 1 , C2 = - 1 5 5 y = e2x - e- 3x 5 5
when, x = 1y = (1) = e2 - e- 3 = 1.4678 5
- Consider the differential equation 3y"(x) + 27y(x) = 0 with initial conditions y(0) and y'(0) = 2000. The value of y at x = 1 is _________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The D.E. is 3y (x) + 27 y (x) = 0
The auxiliary equation is
3 m2 + 27 = 0 m2 + 9 = 0
m = ≠ 3i Solution is y = C1 cos 3x + C2 sin 3x
Given that y (0) = 0
∴ 0 = C1
y' = –3 C1. sin 3x + 3 c2 cos 3x
y' (0) = 2000
2000 = 0 + 3 C2C2 = 2000 3
∴ Solution isy = 2000 sin 3x 3 when x = 1, y = 2000 sin 3 = 94.08 3 Correct Option: A
The D.E. is 3y (x) + 27 y (x) = 0
The auxiliary equation is
3 m2 + 27 = 0 m2 + 9 = 0
m = ≠ 3i Solution is y = C1 cos 3x + C2 sin 3x
Given that y (0) = 0
∴ 0 = C1
y' = –3 C1. sin 3x + 3 c2 cos 3x
y' (0) = 2000
2000 = 0 + 3 C2C2 = 2000 3
∴ Solution isy = 2000 sin 3x 3 when x = 1, y = 2000 sin 3 = 94.08 3
- For a position vector r = xî + yĵ + zk̂ the norm of the vector can be defined as
| r | = √x2 + y2 + z2 . Given a function Φ = In | r |, its gradient ∇Φ is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
r r.r Correct Option: C
r r.r

