Network Elements and the Concept of Circuit
- Find the value of R so that V2 = 2 volt—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given circuit

Apply KCL at node AI 1 + 4 = 2 I1 + V2 R or 4 - 2 = I1 (V2 = 2V) R 4 – 2 = 8 = 5 R 5 
∵ I1 = 10 - 2 = 8 
5 5 or 4R – 2 = 8 R 5
or 20 R – 10 = 8 R
or (20 – 8) R = 10
or 12 R = 10or R = 10 = 5 Ω 12 6 Correct Option: B
Given circuit

Apply KCL at node AI 1 + 4 = 2 I1 + V2 R or 4 - 2 = I1 (V2 = 2V) R 4 – 2 = 8 = 5 R 5 
∵ I1 = 10 - 2 = 8 
5 5 or 4R – 2 = 8 R 5
or 20 R – 10 = 8 R
or (20 – 8) R = 10
or 12 R = 10or R = 10 = 5 Ω 12 6
- For fig. at time t 0 after the switch K was closed, it is found that V2 = + 5 V, determine the value of i 2 (t 0) and d / dt i2 (t 0)—

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given V2 = 5V
I 1 = 10 – V2 = 10 – 5 = 5 1 1 
I 3 = 5 = 2.5 2
I 2 = I1 – I3 = 5 – 2.5 = 2.5 amp.
Voltage across 1 Ω resistance = 2.5 × 1 = 2.5 V
VL = 5 – 2.5 = 2.5 VAlso, VL = L di(t) dt 2.5 = 1 / 2 di2(t0) dt or di2(t0) = 2.5 × 2 = 5 amp/sec dt Correct Option: A
Given V2 = 5V
I 1 = 10 – V2 = 10 – 5 = 5 1 1 
I 3 = 5 = 2.5 2
I 2 = I1 – I3 = 5 – 2.5 = 2.5 amp.
Voltage across 1 Ω resistance = 2.5 × 1 = 2.5 V
VL = 5 – 2.5 = 2.5 VAlso, VL = L di(t) dt 2.5 = 1 / 2 di2(t0) dt or di2(t0) = 2.5 × 2 = 5 amp/sec dt
- The voltage of the source i.e. Vs, if i (t) = – 20 e– 2t
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given i (t) = – 20 e– 2t
V (t) = – 20 e– 2t × 1 = – 20 e– 2t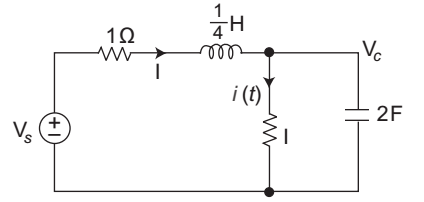
iC = C dV (t) dt = 2. d (– 20 e– 2t) dt
or iC = 80 e– 2t
I = i (t) + i C = – 20 e– 2t + 80 e– 2t
= 60 e– 2t
Vs = VR + VL + V (t)= 1 × 60 e– 2t + L d i + V (t) dt = 1 × 60 e– 2t + 1 d 60 e– 2t – 20 e– t 4 dt
= 60 e– 2t – 15 × 2 e– 2t – 20 e– 2t
= 60 e– 2t – 30e– 2t – 20 e– 2t
= 10e– 2tCorrect Option: A
Given i (t) = – 20 e– 2t
V (t) = – 20 e– 2t × 1 = – 20 e– 2t
iC = C dV (t) dt = 2. d (– 20 e– 2t) dt
or iC = 80 e– 2t
I = i (t) + i C = – 20 e– 2t + 80 e– 2t
= 60 e– 2t
Vs = VR + VL + V (t)= 1 × 60 e– 2t + L d i + V (t) dt = 1 × 60 e– 2t + 1 d 60 e– 2t – 20 e– t 4 dt
= 60 e– 2t – 15 × 2 e– 2t – 20 e– 2t
= 60 e– 2t – 30e– 2t – 20 e– 2t
= 10e– 2t
- Find the Thevenin voltage and resistance for the network shown below across the terminal A.B—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Calculation for Rth
To calculate Rth when dependent source are taking into account for this, assume a imaginary source say 5 V is connected across terminal A and B and current produced by that current source is I then Rth is given by the relation.
Rth = 5/1
the equivalent circuit for calculating Rth is shown below:
5 = 2 Vx + I. 1 ....(i)
Vx = 1. I
5 = 2 I + II = 5 Ω 3 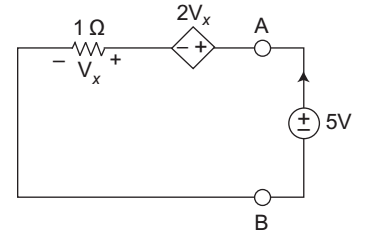
so, Rth = 5 = 3 Ω 5 / 3
Calculation for Vth:
Here the 3 A current source will drop across 1 Ω resistance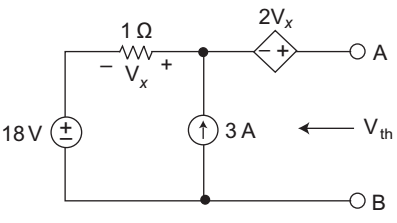
Vx = 3 × 1 = 3 V
or Vth = 2 Vx + Vx + 18
or Vth =3 Vx + 18 = 3 × 3 + 18 = 27 VCorrect Option: A
Calculation for Rth
To calculate Rth when dependent source are taking into account for this, assume a imaginary source say 5 V is connected across terminal A and B and current produced by that current source is I then Rth is given by the relation.
Rth = 5/1
the equivalent circuit for calculating Rth is shown below:
5 = 2 Vx + I. 1 ....(i)
Vx = 1. I
5 = 2 I + II = 5 Ω 3 
so, Rth = 5 = 3 Ω 5 / 3
Calculation for Vth:
Here the 3 A current source will drop across 1 Ω resistance
Vx = 3 × 1 = 3 V
or Vth = 2 Vx + Vx + 18
or Vth =3 Vx + 18 = 3 × 3 + 18 = 27 V
- The Thevenin equivalent of the given at terminal a – b will be—
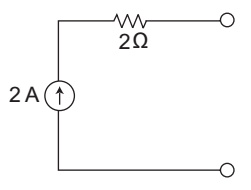
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Because we cannot connect a resistance in series with the current source.
Correct Option: D
Because we cannot connect a resistance in series with the current source.

