Economics miscellaneous
- The law of demand states that
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The law of demand states that, other things remaining the same, the quantity demanded of a commodity is inversely related to its price. Thus, according to the law of demand, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, other things remaining the same.
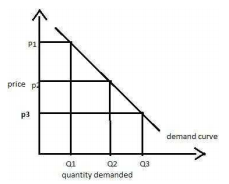
Correct Option: C
The law of demand states that, other things remaining the same, the quantity demanded of a commodity is inversely related to its price. Thus, according to the law of demand, there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded, other things remaining the same.
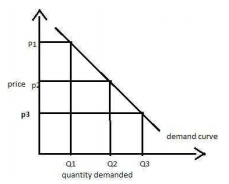
- A ‘Market Economy’ is one which
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
A market economy is an economic system in which economic decisions and the pricing of goods and services are guided solely by the aggregate interactions of a country’s individual citizens and businesses. There is little government intervention or central planning. The United States is the world’s premier market economy.
Correct Option: B
A market economy is an economic system in which economic decisions and the pricing of goods and services are guided solely by the aggregate interactions of a country’s individual citizens and businesses. There is little government intervention or central planning. The United States is the world’s premier market economy.
- Bilateral monopoly situation is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Bilateral monopoly is a market consisting of a single seller (monopolist) and a single buyer (monopsonist).For example, if a single firm produced all the copper in a country and if only one firm used this metal, the copper market would be a bilateral monopoly market. The equilibrium in such a market cannot be determined by the traditional tools of demand and supply.
Correct Option: C
Bilateral monopoly is a market consisting of a single seller (monopolist) and a single buyer (monopsonist).For example, if a single firm produced all the copper in a country and if only one firm used this metal, the copper market would be a bilateral monopoly market. The equilibrium in such a market cannot be determined by the traditional tools of demand and supply.
- From the national point of view, which of the following indicates micro approach?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics in which a variety of economy-wide phenomena is thoroughly examined such as, inflation, price levels, rate of growth, national income, gross domestic product and changes in unemployment. On the other hand, Microeconomics studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. So the study of sales of mobile phones by BSNL comes under microeconomics.
Correct Option: A
Macroeconomics is a branch of economics in which a variety of economy-wide phenomena is thoroughly examined such as, inflation, price levels, rate of growth, national income, gross domestic product and changes in unemployment. On the other hand, Microeconomics studies the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of scarce resources and the interactions among these individuals and firms. So the study of sales of mobile phones by BSNL comes under microeconomics.
- ‘Capital gains’ refers to goods which
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Capital goods are goods that are used in producing other goods, rather than being bought by consumers. They are tangible assets such as buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles and tools that an organization uses to produce goods or services in order to produce consumer goods and goods for other businesses.
Correct Option: C
Capital goods are goods that are used in producing other goods, rather than being bought by consumers. They are tangible assets such as buildings, machinery, equipment, vehicles and tools that an organization uses to produce goods or services in order to produce consumer goods and goods for other businesses.

