Theory of Machines Miscellaneous
- The radius of gyration of a compound pendulum about the point of suspension is 100 mm. The distance between the point of suspension and the centre of mass is 250 mm. Considering the acceleration due to gravity is 9.81 m/s2, the natural frequency (in radian/s) of the compound pendulum is _________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
For compound pendulum,
θ̇̇ + 
mg a 
θ = 0 l
∵ I mk2 = m(0.1)2
I = m(0.01) kg m2
a = 0.250 m
g = 9.81 m/s2θ̇̇ + 
m × 9.81 × 0.250 
= 0 (0.01)m
ωn = √245.25 = 15.660 rad / secCorrect Option: C
For compound pendulum,
θ̇̇ + 
mg a 
θ = 0 l
∵ I mk2 = m(0.1)2
I = m(0.01) kg m2
a = 0.250 m
g = 9.81 m/s2θ̇̇ + 
m × 9.81 × 0.250 
= 0 (0.01)m
ωn = √245.25 = 15.660 rad / sec
- A thin uniform rigid bar of length L and M is hinged at point O, located at a distance of L/3 from one of its ends. The bar is further supported using springs, each of stiffness k located at the two ends. A particle of mass m = M/4 is fixed at one end of the bar, as shown in the figure. For small rotations of the bar about O, the natural frequency of the system is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum

I = (Iabout Ⅰ)rod + (Iabout Ⅰ)point massI = 
ml2 + m 
2l - l 
2 

m 
2l 
2 
12 3 2 4 3 I = ml2 + ml2 = 2ml2 9 9 9
∑MI = 0I θ̇̇ + Kx2 + 2l + kx1 × l = 0 3 3 2ml2 + k 
5 l2 
θ = 0 9 9 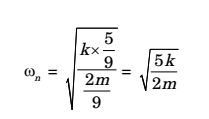
Correct Option: B

I = (Iabout Ⅰ)rod + (Iabout Ⅰ)point massI = 
ml2 + m 
2l - l 
2 

m 
2l 
2 
12 3 2 4 3 I = ml2 + ml2 = 2ml2 9 9 9
∑MI = 0I θ̇̇ + Kx2 + 2l + kx1 × l = 0 3 3 2ml2 + k 
5 l2 
θ = 0 9 9 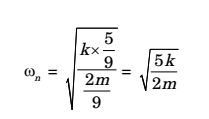
- A mass m is attached to two identical springs having constant k as shown in the figure. The natural frequency ω of this single degree of freedom system is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
keq = k1 + k2

Correct Option: A
keq = k1 + k2

- The static deflection of a spring under gravity, when a mass of 1 kg is suspended from it, is 1 mm. Assume the acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2. The natural frequency of this springmass system (in rad/s) is _______
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
g = 10 m/s2, m = 1 kg
Deflection: ∆ = 1 mm
= 100 rad /secCorrect Option: A
g = 10 m/s2, m = 1 kg
Deflection: ∆ = 1 mm
= 100 rad /sec
- The system shown in the figure consists of block A of mass 5 kg connected to a spring through a massless rope passing over pulley B of radius r and mass 20 kg. The spring constant k is 1500 N/m. If there is no slipping of the rope over the pulley, the natural frequency of the system is _______ rad/s.

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
KE = 1 m ẋ2 + 1 I θ̇2 2 2 m = 5 kg , θ = x r I = 20 × r2 = 10r2 2 KE = 1 5 ẋ2 + 1 10r2 . ẋ2 = 1 (15) ẋ2 2 2 r2 2
∴ meq = 15PE = 1 kx2 2
∴ keq = k = 1500 N / m
Natural frequency
= 10 rad /secCorrect Option: B
KE = 1 m ẋ2 + 1 I θ̇2 2 2 m = 5 kg , θ = x r I = 20 × r2 = 10r2 2 KE = 1 5 ẋ2 + 1 10r2 . ẋ2 = 1 (15) ẋ2 2 2 r2 2
∴ meq = 15PE = 1 kx2 2
∴ keq = k = 1500 N / m
Natural frequency
= 10 rad /sec

