Theory of Machines Miscellaneous
- A slider crank mechanism has slider mass of 10 kg, stroke of 0.2 m and rotates with a uniform angular velocity of 10 rad/s. The primary inertia forces of the slider are partially balanced by a revolving mass of 6 kg at the crank, placed at a distance equal to crank radius. Neglect the mass of connecting rod and crank. When the crank angle (with respect to slider axis) is 30°, the unbalanced force (in newton) normal to the slider axis is __________.
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
r = 0.2 = 0.1 2
Now m= 6kg
F = mr (102) sin θ
= 6 × 0.1 × 100 × sin 30° = 30 NCorrect Option: A
r = 0.2 = 0.1 2
Now m= 6kg
F = mr (102) sin θ
= 6 × 0.1 × 100 × sin 30° = 30 N
- For a four bar linkage in toggle position, the value of mechanical advantage is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Mechanical advantages
= Load (output force) Effort (input force)
For a four bar linkage in toggle position, effort = 0
∴ Mechanical Advantage = ∞Correct Option: D
Mechanical advantages
= Load (output force) Effort (input force)
For a four bar linkage in toggle position, effort = 0
∴ Mechanical Advantage = ∞
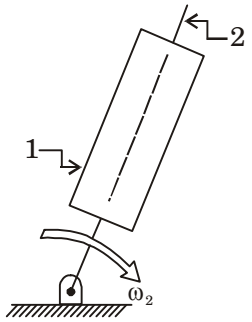
- In the figure shown, the relative velocity of link 1 with respect of link 2 is 12 m/s. Link 2 rotates at a constant speed of 120 rpm. The magnitude of Coriolis component of acceleration of link 1 is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Velocity of link 1 with respect to link 2,
V½ = 12 m/sω = 2πN = 2π × 120 = 4π 60 60
∴ Corioli’s component of acceleration
= 2V½ω = 2 × 12 × 4π
= 301.59 ≈ 302 m/s2Correct Option: A
Velocity of link 1 with respect to link 2,
V½ = 12 m/sω = 2πN = 2π × 120 = 4π 60 60
∴ Corioli’s component of acceleration
= 2V½ω = 2 × 12 × 4π
= 301.59 ≈ 302 m/s2
- The circular disc shown in its plan view in the figure rotates in a plane parallel to the horizontal plane about the point O at a uniform angular velocity ω. Two other points A and B are located on the line OZ at distances rA and rB from O respectively.

The acceleration of point B with respect to point A is a vector of magnitude
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Acceleration of point B with respect to point A
αB/A = ω × υB/A
= ω × ω (rB - rA)
= ω2 (rB - rA)
and direction from Z to O.Correct Option: D
Acceleration of point B with respect to point A
αB/A = ω × υB/A
= ω × ω (rB - rA)
= ω2 (rB - rA)
and direction from Z to O.
- A four bar mechanism is shown in the figure. The link numbers are mentioned near the links. Input link 2 is rotating anticlockwise with a constant angular speed ω2. Length of different links are
O2O4 = O2 A = L,
AB = O4 B = 2 L
The magnitude of the angular speed of the output link 4 is ω4 at the instant when link 2 makes an angle of 90° with O2O4 as shown. The ratioω4 is ω2
_____ (round off to two decimal places).
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum


Now, O4C = cos 75°
O4C = sin 75°
∆AO2I24 ≈ ∆BI24CL = √2Lsin75° x x + L + √2cos75° 
⇒ L = 0.2679 x ω4 = 1 = 0.7887 ≈ 0.79 ω2 1 + 0.267 Correct Option: A


Now, O4C = cos 75°
O4C = sin 75°
∆AO2I24 ≈ ∆BI24CL = √2Lsin75° x x + L + √2cos75° 
⇒ L = 0.2679 x ω4 = 1 = 0.7887 ≈ 0.79 ω2 1 + 0.267

