Physics miscellaneous
- If density of oxygen is 16 times that of hydrogen, what will be their corresponding ratio of velocity of sound?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The velocity of sound in a gas is given by
....(i)v = γp ρ
Clearly, velocityv is inversely proportional to the square root of density (r) of the gas. Now, let us consider two gases which are at the same pressure (P) and the same value of g. If r1 and r2 be their densities, then velocity of sound in the two gases arev1 = √ γp ρ1 and v2 = √ γp ρ2
....(ii)∴ v1 = √ ρ2 v2 ρ1
For example, density of oxygen is 16 times the density of hydrogen, therefore from (ii), we havevH = √ ρo vo ρH = √ 16pH = 4 PpH
or vH = 4vo
So the corresponding ration of velocity of sound in oxygen and hydrogen is 1:4.Correct Option: D
The velocity of sound in a gas is given by
....(i)v = γp ρ
Clearly, velocityv is inversely proportional to the square root of density (r) of the gas. Now, let us consider two gases which are at the same pressure (P) and the same value of g. If r1 and r2 be their densities, then velocity of sound in the two gases arev1 = √ γp ρ1 and v2 = √ γp ρ2
....(ii)∴ v1 = √ ρ2 v2 ρ1
For example, density of oxygen is 16 times the density of hydrogen, therefore from (ii), we havevH = √ ρo vo ρH = √ 16pH = 4 PpH
or vH = 4vo
So the corresponding ration of velocity of sound in oxygen and hydrogen is 1:4.
- The redness in atmosphere at Sunrise and Sunset is due to :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The red colour in the sky at sunset (and sunrise) is due to an effect called Rayleigh scattering. At sunrise or sunset, since the Sun is low on the horizon, the light rays must pass through more of the atmosphere – and therefore bounce off more molecules – than at other times of day. Thus, blue light gets scattered away before the light reaches your eyes. Other colors – such as red, orange and yellow –continue to pass through the atmosphere unaffected.
Correct Option: D
The red colour in the sky at sunset (and sunrise) is due to an effect called Rayleigh scattering. At sunrise or sunset, since the Sun is low on the horizon, the light rays must pass through more of the atmosphere – and therefore bounce off more molecules – than at other times of day. Thus, blue light gets scattered away before the light reaches your eyes. Other colors – such as red, orange and yellow –continue to pass through the atmosphere unaffected.
- Distant objects are visible as a little out of focus in this condition :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and shortsightedness, is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in front of it, causing the image that one sees when looking at a distant object to be out of focus, but in focus when looking at a close object.
Correct Option: D
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and shortsightedness, is a condition of the eye where the light that comes in does not directly focus on the retina but in front of it, causing the image that one sees when looking at a distant object to be out of focus, but in focus when looking at a close object.

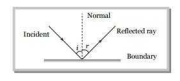
- A light wave is incident over a plane surface with velocity x. After reflection the velocity becomes :
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
When a ray of light incident on a boundary separating two media comes back into the same media, this phenomenon, is called reflection of light. After reflection velocity, wavelength and frequency of light remains same but intensity decreases.
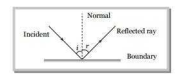
Correct Option: B
When a ray of light incident on a boundary separating two media comes back into the same media, this phenomenon, is called reflection of light. After reflection velocity, wavelength and frequency of light remains same but intensity decreases.
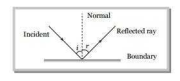
- In which region of electromagnetic spectrum does the Lyman series of hydrogen atom lie ?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In physics and chemistry, the Lyman series is a hydrogen spectral series of transitions and resulting ultraviolet emission lines of the hydrogen atom as an electron goes from n > 2 to n = 1 (where n is the principal quantum number) the lowest energy level of the electron. The first line in the spectrum of the Lyman series was discovered in 1906 by Harvard physicist Theodore Lyman, while studying the ultraviolet spectrum of electrically excited hydrogen gas. The rest of the lines of the spectrum (all in the ultraviolet) were discovered by Lyman from 1906-1914.
Correct Option: C
In physics and chemistry, the Lyman series is a hydrogen spectral series of transitions and resulting ultraviolet emission lines of the hydrogen atom as an electron goes from n > 2 to n = 1 (where n is the principal quantum number) the lowest energy level of the electron. The first line in the spectrum of the Lyman series was discovered in 1906 by Harvard physicist Theodore Lyman, while studying the ultraviolet spectrum of electrically excited hydrogen gas. The rest of the lines of the spectrum (all in the ultraviolet) were discovered by Lyman from 1906-1914.

