Physics miscellaneous
- Which of the following is not true about X-rays?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
X-rays and gamma rays are photons, i.e. highenergy light-waves. When emitted by a source, for example, radium or cobalt, located outside the body, they easily pass through the body, hence they are usually called penetrating radiation. Because X-rays are penetrating, they can be used in diagnostic medicine to image human bones or human organs made opaque by a dye.
Correct Option: A
X-rays and gamma rays are photons, i.e. highenergy light-waves. When emitted by a source, for example, radium or cobalt, located outside the body, they easily pass through the body, hence they are usually called penetrating radiation. Because X-rays are penetrating, they can be used in diagnostic medicine to image human bones or human organs made opaque by a dye.
- The colour of the ocean appears to be blue because the sunlight falling on it is
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The reason the ocean is blue is due to the absorption and scattering of light. The blue wavelengths of light are scattered, similar to the scattering of blue light in the sky but absorption is a much larger factor than scattering for the clear ocean water. In water, absorption is strong in the red and weak in the blue, thus red light is absorbed quickly in the ocean leaving blue. The red, yellow, and green wavelengths of sunlight are absorbed by water molecules in the ocean.
Correct Option: D
The reason the ocean is blue is due to the absorption and scattering of light. The blue wavelengths of light are scattered, similar to the scattering of blue light in the sky but absorption is a much larger factor than scattering for the clear ocean water. In water, absorption is strong in the red and weak in the blue, thus red light is absorbed quickly in the ocean leaving blue. The red, yellow, and green wavelengths of sunlight are absorbed by water molecules in the ocean.
- Where do the electrical charges reside in a charged conductor?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
In all conductors, charges reside on the surface. The reason for this is that conductors have free electrons, that is, the electrons are loosely attached to the nucleus of the atoms in the conductors. When a solid conductor in equilibrium carries a net charge, the charge resides on the outer surface of the conductor. Besides, the electric field just outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface and that the field inside is zero.
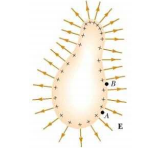
Correct Option: D
In all conductors, charges reside on the surface. The reason for this is that conductors have free electrons, that is, the electrons are loosely attached to the nucleus of the atoms in the conductors. When a solid conductor in equilibrium carries a net charge, the charge resides on the outer surface of the conductor. Besides, the electric field just outside the conductor is perpendicular to the surface and that the field inside is zero.
- The point where total mass of a body is supposed to be concentrated is known as
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The centre of mass of a body or a system of particles is defined as a single point at which the whole mass of the body or system is imagined to be concentrated and all the applied forces acts at that point. It is that point that moves when forces are applied on the body.
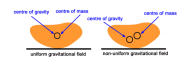
Correct Option: B
The centre of mass of a body or a system of particles is defined as a single point at which the whole mass of the body or system is imagined to be concentrated and all the applied forces acts at that point. It is that point that moves when forces are applied on the body.
- The temperature of a liquid is 32° F. What is its temperature in Celsius scale?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The formulas for converting between degree Celsius and degree Fahrenheit are: °F = °C 9/5 + 32 and °C = (°F - 32) 5/9. So in Celsius scale, 32o F= 0° C
Correct Option: B
The formulas for converting between degree Celsius and degree Fahrenheit are: °F = °C 9/5 + 32 and °C = (°F - 32) 5/9. So in Celsius scale, 32o F= 0° C

