Control system miscellaneous
-
A system with the open loop transfer function G(s) = K s(s + 2)(s2 + 2s + 2)
is connected in a negative feedback configuration with a feedback gain of unity. For the closed loop system to be marginally stable, the value of K is ____
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Characteristic equation is, 1 + G(s)H(s) = 0
⇒ 1 + G(s) = 0 (∴ H(s) = 1)⇒ 1 + k = 0 s(s + 2)(s2 + 2s + 2)
⇒ s4 + 4s3 + 6s2 + 4s + k = 0
Constructing Routh- array, we have
For the closed loop system to be marginally stable, 20 – 4k = 0
⇒ k = 5Correct Option: D
Characteristic equation is, 1 + G(s)H(s) = 0
⇒ 1 + G(s) = 0 (∴ H(s) = 1)⇒ 1 + k = 0 s(s + 2)(s2 + 2s + 2)
⇒ s4 + 4s3 + 6s2 + 4s + k = 0
Constructing Routh- array, we have
For the closed loop system to be marginally stable, 20 – 4k = 0
⇒ k = 5
-
The system ẋ = Ax + Bu with A = 
-1 2 
, B = 
0 
is 0 2 1
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given : ẋ = Ax + Bu ;
A = 
-1 2 
, B = 
0 
0 2 1
For stability, characteristic equation
∴ M = (s + 1) × (s – 2) = 0
⇒ (s – 2) (s + 1) = 0
⇒ s = 2, s = – 1
So one root in right hand side of s-plane, so system is unstable.For controllability : B = 
0 
1 AB = 
-1 2 

0 
= 
2 
0 2 1 2 
= 0 – 2 = – 2 ≠ 0
So controllable.
Correct Option: C
Given : ẋ = Ax + Bu ;
A = 
-1 2 
, B = 
0 
0 2 1
For stability, characteristic equation
∴ M = (s + 1) × (s – 2) = 0
⇒ (s – 2) (s + 1) = 0
⇒ s = 2, s = – 1
So one root in right hand side of s-plane, so system is unstable.For controllability : B = 
0 
1 AB = 
-1 2 

0 
= 
2 
0 2 1 2 
= 0 – 2 = – 2 ≠ 0
So controllable.
- The characteristic equation of a closed-loop system is s(s + 1)(s + 3) + k(s + 2) = 0, k > 0. Which of the following statements is true?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given : s(s + 1) (s + 3) + k(s + 2) = 0; k > 0
⇒ 1 + k(s + 2) = 0 s(s + 1)(s + 3)
But 1 + G(s) H(s) = 0∴ G(s) H(s
) =k(s + 2) s(s + 1)(s + 3)
Roots s = 0, s = – 1, s = – 3 (poles); s = – 2 (zero)
It has real pole or zeros.φA = 2q + 1 × 180° n - m 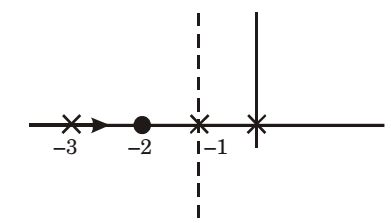
At s = 0, Asymptotesφ0 = (2*0 + 1)180 = 90° 2 At s = 1, φ1 = (2*1 + 1)180 = 270° 2
Centroid,(-σA) = ∑ real parts of poles - ∑ real poles of zeros number of poles - number of zeros
∴ Re[s] = – 1Correct Option: C
Given : s(s + 1) (s + 3) + k(s + 2) = 0; k > 0
⇒ 1 + k(s + 2) = 0 s(s + 1)(s + 3)
But 1 + G(s) H(s) = 0∴ G(s) H(s
) =k(s + 2) s(s + 1)(s + 3)
Roots s = 0, s = – 1, s = – 3 (poles); s = – 2 (zero)
It has real pole or zeros.φA = 2q + 1 × 180° n - m 
At s = 0, Asymptotesφ0 = (2*0 + 1)180 = 90° 2 At s = 1, φ1 = (2*1 + 1)180 = 270° 2
Centroid,(-σA) = ∑ real parts of poles - ∑ real poles of zeros number of poles - number of zeros
∴ Re[s] = – 1
- The measurement system shown in the figure uses three sub-systems in cascade whose gains are
specified as G1,G2 and 1 G3
The relative small errors associated with each respective subsystem G1 , G2 and G3 are ε1 , ε2 and ε3. The error associated with the output is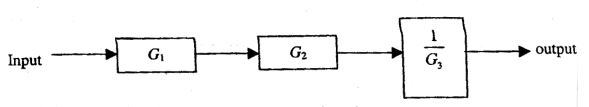
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The relative error of product or division of different quantities is equal to the sum of relative errors of individual quantities.
Correct Option: D
The relative error of product or division of different quantities is equal to the sum of relative errors of individual quantities.
- The polar plot of an open loop stable system is shown below. The closed loop system is

-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: D
NA

