Signal and systems miscellaneous
- What is the output of the system with
h[n] = 
1 
2 u(n) 2
in response to the inputx[n] = 3 + cos 
πn + π 
? 3
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
NA
Correct Option: B
NA
- A discrete time system has impulse response h[n] = αnu(n + 2), |α| < 1. Which one of the following is correct?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given
h(n) = an u(n + 2), |a| < 1
● As given that |a| < 1, therefore, the system is obviously stable.
● Non-causal since output depends upon the future value for any value of n.
● Given system possess memory,
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.Correct Option: C
Given
h(n) = an u(n + 2), |a| < 1
● As given that |a| < 1, therefore, the system is obviously stable.
● Non-causal since output depends upon the future value for any value of n.
● Given system possess memory,
Hence, alternative (C) is the correct choice.
- Consider the following statements about the z-transform, X(z) of the sequence
x(n) = 0 for n < 0 = 2n for n ≥ 0
(ROC denotes region of convergence in the z-plane)1. X(z) = 1 ROC: |z| > 2 1 – 2z– 1 2. X(z) = 1 + 2z– 1 ROC: |z| > 2 1 – 2z– 1
3. X(z) = 1 ROC: |z| > 2 1 – 2z– 1
Which of these statements are correct?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
Given,
x(t) = 
2n; 2n, for n ≥ 0 0, for n < 0
thenX(z) = z = 1 |z| > 2 z - 2 1 - 2z-1 (1) X(z) = 1 ROC, |z| > 2 → is true 1 - 2z-1 (2) X(z) = 1 + 2z-1 ROC : |z| > 2 1 - 2z-1 = 1 - 2z-1 + 2z-1 ; ROC : |z| > 2 1 - 2z-1 = 1 ;ROC: |z| > 2 → Also true 1 - 2z-1
(3) is not true since x(n) = 0 for n < 0.
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.Correct Option: B
Given,
x(t) = 
2n; 2n, for n ≥ 0 0, for n < 0
thenX(z) = z = 1 |z| > 2 z - 2 1 - 2z-1 (1) X(z) = 1 ROC, |z| > 2 → is true 1 - 2z-1 (2) X(z) = 1 + 2z-1 ROC : |z| > 2 1 - 2z-1 = 1 - 2z-1 + 2z-1 ; ROC : |z| > 2 1 - 2z-1 = 1 ;ROC: |z| > 2 → Also true 1 - 2z-1
(3) is not true since x(n) = 0 for n < 0.
Hence, alternative (B) is the correct choice.
- Which one of the following gives the linear convolution of two finite length sequences x(n) = {1, 3, 1, 2} and y(n) = {1, 2, 3}?
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
The linear convolution of x(n) and y(n) can be given as
∞ r(n) = 
x(k) y(n – k) n = – ∞ 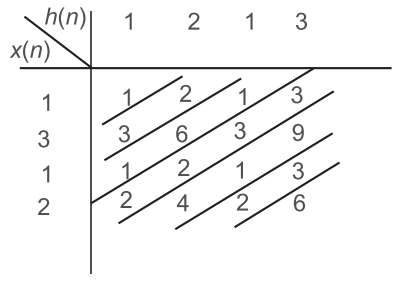
r(n) = 1 (3 + 2) (1 + 6 + 1) (2 + 2 + 3 + 3) (4 + 1 + 9) (2 + 3) 6
or r(n) = {1 5 8 10 14 5 6}Correct Option: D
The linear convolution of x(n) and y(n) can be given as
∞ r(n) = 
x(k) y(n – k) n = – ∞ 
r(n) = 1 (3 + 2) (1 + 6 + 1) (2 + 2 + 3 + 3) (4 + 1 + 9) (2 + 3) 6
or r(n) = {1 5 8 10 14 5 6}
- Z transform and associated ROC for the sequence x[n] = a– n u[– n] is—
-
View Hint View Answer Discuss in Forum
As we know that
x[n] = an u[n] ←z→ z = x(z), |z| > |a| z - a
By using time reversal propertyx[- n] ←z→ z = x(z), |z| < |a| z - a So, a–n u[– n]←z→ z- 1 =|z| < 1 z- 1 - a |a|
oror, a–n u[– n]←→ 1 1 - az
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.Correct Option: D
As we know that
x[n] = an u[n] ←z→ z = x(z), |z| > |a| z - a
By using time reversal propertyx[- n] ←z→ z = x(z), |z| < |a| z - a So, a–n u[– n]←z→ z- 1 =|z| < 1 z- 1 - a |a|
oror, a–n u[– n]←→ 1 1 - az
Hence, alternative (D) is the correct choice.

