-
Consider the following C program segment where CellNode represents a node in a binary tree :
struct Cell Node {
struct Cell Node *leftChild;
int element; struct CellNode *rightChild;
}
int GetValue (struct CellNode *ptr) {
int value = 0
if (ptr! = NULL)
if ((ptr - > leftChild = = NULL) &&
(ptr -> rightChild == NULL) {
value = 1;
else
value = value + GetValue (ptr -> leftChild)
+ GetValue (ptr -> rightChild);
}
return (value);
}
The value returned by GetValue when a pointer to the root of a binary tree is passed as its argument is
-
- the number of nodes in the tree
- the number of internal nodes in the tree
- the number of leaf nodes in the tree
- the height of the tree
- the number of nodes in the tree
Correct Option: C
A node is a leaf node if both left and right child nodes of it are NULL.
1) If node is NULL then return 0.
2) Else If left and right child nodes are NULL return 1.
3) Else recursively calculate leaf count of the tree using below formula.
Leaf count of a tree = Leaf count of left subtree + Leaf count of right subtree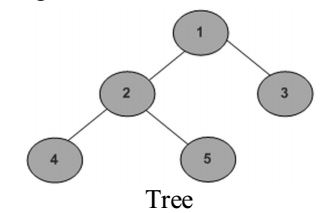
Leaf count for the above tree is 3.

