Direction: A refrigerator based on ideal vapour compression cycle operates between the temperature limits of –20°C and 40°C. The refrigerant enters the condenser as saturated vapour and leaves as saturated liquid. The enthalpy and entropy values for saturated liquid and vapour at these temperatures are given in the table below.
| T | hf | hg | sf | sg |
| (°C) | (kJ/kg) | (kJ/kg) | (kJ/kgK) | (kJ/kgK) |
| –20 | 20 | 180 | 0.07 | 0.7366 |
| 40 | 80 | 200 | 0.3 | 0.67 |
-
If refrigerant circulation rate is 0.025 kg/s, the refrigeration effect is equal to
-
- 2.1 kW
- 2.5 kW
- 3.0 kW
- 4.0 kW
- 2.1 kW
Correct Option: A
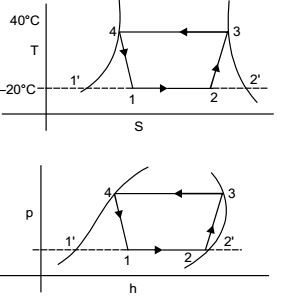
h1 = h4 = 80 kJ/kg , s3 = 0.67
h3 = 200 kJ/kg , s2 = 0.67
h1' = 20 kJ/kg , s2' = 0.7366
h2' = 20 kJ/kg , s1' = 0.07
s2 = s1' + x(s2' - s1')
= 0.07 + x + (0.7366 – 0.07)
⇒ 0.67 = 0.07 + 0.6666 x
| ⇒ x = | = 0.90 | |
| 0.6666 |
h2 = h1' + x(h2' - h1')
= 20 + 0.9(180 – 20)
= 20 + 0.9 × 160 = 165 kJ/kg
Refrigerating effect per kg = h2 – h1 = 164 – 80 = 84 kJ/kg
Hence refrigerating effect for 0.025 kg/sec circulation = 84 × 0.025 = 2.1 kW

